| Commercial health insurance in India refers to health coverage provided by private sector insurers or by government-owned, public sector insurers operating on a profit-driven basis. Unlike government schemes such as Ayushman Bharat, commercial health insurance is open to all individuals, families, or groups and offers customizable plans like individual, family floater, critical illness, and super top-up policies. It typically covers hospitalization, surgeries, daycare procedures, and sometimes outpatient care, with premiums regulated by the IRDAI. |
Imagine facing a medical emergency without any financial backup. Unfortunately, this is a reality for over 40 crore Indians. According to research reports by the National Insurance Academy, about 31% of the Indian population lacks any form of health insurance.
Although the government has launched health schemes to bridge this gap, the problem still persists. In response, commercial health insurance provides a crucial financial safety net when you need it most.
In this guide, we cover:
- What commercial health insurance is and how it works in India
- Key benefits and features to look out for when buying a policy
- The different types of commercial plans available (from family floaters to super top-ups)
- How insurers calculate your premiums using risk and underwriting models
- Standard exclusions and policy loopholes you should know
- A simple step-by-step guide to enrolling in the right plan for you
Whether you’re buying insurance for the first time or upgrading your existing coverage, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know.
Looking for the right health insurance plan for you and your family? Book a free consultation with Ditto today, and let us help you find the best coverage options tailored to your needs.
What is Commercial Health Insurance?
Commercial health insurance in India refers to health coverage provided by private, non-governmental insurers. These can include both public sector general insurers, such as New India and Oriental, as well as private companies like HDFC ERGO and Aditya Birla Health Insurance.
Unlike public schemes, which are government-subsidized and often have specific eligibility criteria, commercial health insurance policies tend to be more flexible in their requirements. They can be tailored to suit various needs, including individual plans, family floater plans, or group policies, and operate under the oversight of the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI).
With the recent removal of 18% GST on personal retail health insurance plans, premiums are now significantly more affordable and accessible to a broader population. Now, you can get the same coverage at a lower cost.
Understanding what commercial health insurance is sets the foundation for informed decision-making. But how does it actually operate in real life when claims are made, and bills need to be paid? Let’s break it down.
How Commercial Health Insurance Works
Commercial health insurance works on the principle of risk pooling, where individuals or families pay premiums to an insurer in exchange for financial protection against healthcare costs. When an insured person requires medical treatment, the insurer helps cover the costs, as outlined in the policy terms.
So, why should someone consider buying a commercial health insurance policy? Here are some of the core benefits that make these plans a wise financial choice.
Key Benefits of Commercial Health Insurance
- Financial protection against unexpected medical costs.
- Access to premium healthcare services and cashless treatment at network hospitals.
- Tax deductions under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act (under the old regime).
- Comprehensive coverage for hospitalization, daycare procedures, surgeries, and sometimes even outpatient care.
Essential Features to Look Out For in a Commercial Health Insurance
1) Network Hospitals:
Ensure the insurer has a wide range of hospitals in its network, so you have flexibility in choosing treatment facilities.
Ditto’s Tip: Always check if your preferred hospital is part of the insurer’s network. This ensures smooth and easy cashless treatment. Ideally, you should look for insurers with more than 10,000+ network hospitals.
2) Waiting Period:
Most policies have a waiting period for pre-existing diseases (up to 3 years) and specific illnesses (up to 2 years). However, this isn’t the whole picture.
Many insurers now offer add-ons that allow you to reduce or even waive these waiting periods by paying an additional premium. For example, Care Health Insurance offers three add-ons to minimize waiting periods under plans like Care Supreme, which serve different purposes. Aditya Birla, on the other hand, provides flexible add-ons that can reduce the premium to as low as one year.
3) Co-payment:
Some policies require you to bear a percentage of the claim amount. Make sure you understand how this works.
Ditto’s Tip: Try to avoid opting for a copayment unless it is absolutely necessary. If you want to learn more, you can read our detailed guide on Copayment in Health Insurance.
Note: You should also avoid room-rent limits and disease-wise sub-limits.
4) Add-ons:
Additional cover options, like consumables, super bonus, critical illness, maternity benefits, and hospital cash, may be available.
Ditto’s Tip: While add-ons and riders are beneficial to have, it is crucial to understand the riders you actually need. We typically recommend the following:
- Unlimited Restoration
- Super bonus or bonus enhancer ride
- PED Waiting period reduction rider if you have a PED
- Consumables cover

5) Exclusions to Be Aware Of
- Cosmetic treatments or Experimental Procedures:
Procedures like plastic surgery (unless medically necessary) aren’t typically covered.
- Suicide/Self-Harm
Coverage is usually not provided for any claims related to suicide or self-inflicted injuries.
- War/Terrorism
Injuries or damage caused by acts of war, terrorism, or related incidents are generally excluded from coverage.
- High-risk activities:
Insurers do not cover accidents from dangerous sports or activities done as a profession.
Check out our detailed blog on Permanent Exclusions in Health Insurance to get a better understanding of this.
Now that you know the pros, cons, and fine print, let’s explore the types of commercial health insurance plans available in India.
What are the different types of commercial health insurance plans?
In India, commercial health insurance offers a wide range of plans designed to meet various needs. These can include:
1) Individual Health Insurance:
Covers a single person, offering customized benefits and premium rates based on personal health factors.
2) Family Floater Plans:
A single policy that covers an entire family, with a shared sum insured amount.
3) Standalone Critical Illness Plans:
Offers coverage for specific critical illnesses such as cancer, stroke, heart attacks, etc.
4) Top-Up and Super Top-Up Plans:
Provide extra coverage above a deductible threshold, at a lower cost.
5) Group Health Insurance:
Usually offered by employers to their employees (in a large group), typically at a lower premium due to the group policy and immediate coverage (with no waiting periods).
Note: The lower premiums are possible because the risk is spread across a large pool of people, reducing the insurer's overall liability.
To learn about these plans in detail, you can check out our guide on Types of Health Insurance in India.
Have you ever wondered why two people can pay different premiums for seemingly similar coverage? The answer lies in how insurers assess risk and calculate premiums.
Understanding Risk Management and Premium Pricing in Commercial Health Insurance
Let’s unpack how it works.
1) Risk Pooling
Insurers rely on the concept of risk pooling to function. By gathering premiums from a large pool of policyholders, insurers create a fund that can be used to cover the medical expenses of a smaller subset of individuals who need healthcare services.
2) Underwriting and Premium Setting
Premiums are determined by actuaries, who analyze risk data to predict the potential claims the insurer may face. Factors such as age, health history, location, and lifestyle habits affect the cost of premiums. The IRDAI oversees the approval process for premiums and their hikes to ensure fairness and transparency.
3) Reinsurance
Insurers transfer part of their risk to larger reinsurers to minimize financial exposure in the event of large-scale claims.
With a better grasp of how premiums are priced and risk is managed, the next logical step is understanding how to actually get insured.
How To Enroll in Commercial Health Insurance?
Here's how to enroll in a commercial health plan.
1) Choose a Plan:
Based on your medical needs and budget, determine whether an individual or family floater plan is best for you.
2) Fill Proposal Form:
Provide accurate health and lifestyle details in the form.
3) Underwriting Process:
The insurer assesses the application and determines the premium, coverage, and terms based on your risk profile.
4) Issuance of Policy:
Once the insurer reviews your application, it may fall into one of the following four classifications:
- Accepted
The application is approved without any changes. You will receive the health insurance policy outlining all terms, conditions, and coverage limits.
- Loading
The application is approved, but an additional premium is due due to higher risk (e.g., pre-existing conditions or lifestyle factors).
- Permanent Exclusion
The policy is issued, but specific illnesses or conditions are permanently excluded from coverage.
- Rejection
The insurer declines to issue a policy based on underwriting guidelines.
Commercial insurance is just one piece of the puzzle. To understand its full value, it's essential to consider how it aligns with government-sponsored healthcare schemes in India.
What is the Role of Government Health Insurance?
Government schemes prioritize social equity by providing health coverage to economically disadvantaged segments of society. These schemes provide access to primary healthcare, maternal care, and basic treatments, often in areas where private insurers do not operate. Their reach is vast, and they aim to reduce financial burdens caused by medical emergencies in underserved populations.
Next, let’s examine how commercial health insurance complements public coverage.
What is the Role of Commercial Health Insurance?
In the current healthcare ecosystem, most Indians fall into a coverage gap: they’re not poor enough to qualify for government schemes, but not wealthy enough to comfortably afford out-of-pocket private care for serious illnesses. These are the salaried professionals, gig workers, small business owners, and informal sector workers who are most vulnerable to unexpected healthcare costs.
Until India achieves proper universal healthcare, where everyone is covered regardless of income or employment status, commercial insurance serves as a necessary bridge. It helps
- Reduce dependency on overcrowded public hospitals where treatment may be delayed due to long queues or resource shortages.
- Ensure continuity of care, particularly for chronic diseases or advanced treatments that necessitate regular follow-up and specialist intervention.
- Expand choice and autonomy, allowing individuals to choose better-equipped hospitals, reputed doctors, and timely medical attention without being forced into the public system.
- Promote financial stability by shielding families from health-related poverty or debt traps during medical emergencies.
In essence, commercial health insurance is no longer a privilege; it’s a practical safeguard. Until public healthcare infrastructure and funding catch up to the country's growing demands, opting into a well-structured commercial health insurance plan is one of the smartest financial decisions most Indians can make today.
Why Choose Ditto for Health Insurance
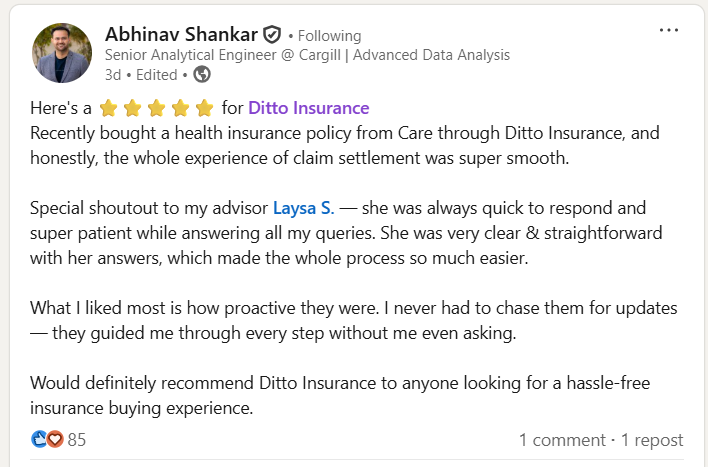
At Ditto, we’ve assisted over 7,00,000 customers with choosing the right insurance policy. Why customers like Abhinav below love us:
✅No-Spam & No Salesmen
✅Rated 4.9/5 on Google Reviews by 15,000+ happy customers
✅Backed by Zerodha
✅Dedicated Claim Support Team
✅100% Free Consultation
You can book a FREE consultation. Slots are running out, so make sure you book a call now!
Conclusion
Both government and commercial health insurance play essential roles in India’s healthcare ecosystem. While government schemes like Ayushman Bharat ensure universal access to healthcare for low-income populations, commercial insurance helps fill in the gaps, offering additional coverage, better access to private healthcare, and a wider range of benefits.
In the end, a combination of both public and private insurance can provide a robust, well-rounded approach to healthcare, benefiting the entire population.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between commercial and private health insurance?
While all commercial health insurance is private, "private health insurance" typically refers to individual insurers offering health policies, whereas "commercial" insurance encompasses both private companies and public sector insurers that operate for profit.
How do health insurers earn money?
Health insurers earn money primarily through the collection of premiums from policyholders. They pool this money to cover the claims of those who fall ill or need treatment. Insurers invest a portion of these funds to generate additional income.
In simple terms: If they collect ₹100 in premiums and pay out ₹70 in claims, the remaining ₹30 (minus admin costs) is their profit margin.
What is a health insurance agent? How is health insurance sold?
A health insurance agent is a licensed intermediary who helps individuals or businesses choose and buy health insurance policies. They act as a bridge between the insurer and the customer, explaining policy terms, comparing options, and assisting in enrollment.
Health insurance is sold through multiple channels: individual agents or brokers, corporate agents, online platforms, bancassurance, and direct-to-customer sales from insurer websites.
Agents usually earn commissions based on the premiums of the policies they sell.
How does a health insurance claim work?
When you need medical care, you can file a cashless or reimbursement claim, depending on the hospital and policy terms.
- In cashless claims, the insurer directly settles the bill with the hospital (only at network hospitals).
- In reimbursement claims, you pay upfront and submit documents to get reimbursed.
What is the role of a TPA?
A TPA (Third Party Administrator) acts as the middleman between the hospital and the insurer. They assist in processing claims, verifying documentation, and ensuring timely approvals.
What are the types of commercial health insurers in India?
In India, commercial health insurers are divided into two major segments:
- General Insurance Companies
These insurers offer health insurance in conjunction with other products, such as motor, travel, and property insurance.
Examples: HDFC ERGO, ICICI Lombard, Bajaj Allianz.
- Standalone Health Insurance Companies (SAHIs)
These insurers specialize exclusively in health insurance and related products.
Examples: Niva Bupa, Care Health, Star Health, Aditya Birla Health.
SAHIs tend to offer more product depth, better disease-specific plans, and innovation tailored to healthcare needs.
Last updated on:










