Quick Overview
Confused whether to go for a comprehensive health plan that covers your medical bills from the 1st rupee you spend or opt for a deductible? At Ditto, we guide thousands of customers and help them purchase the correct health plan. This guide walks you through the types of deductibles, how they work, and do they align with your future needs.
What Is Deductible in Health Insurance and How Does It Work?
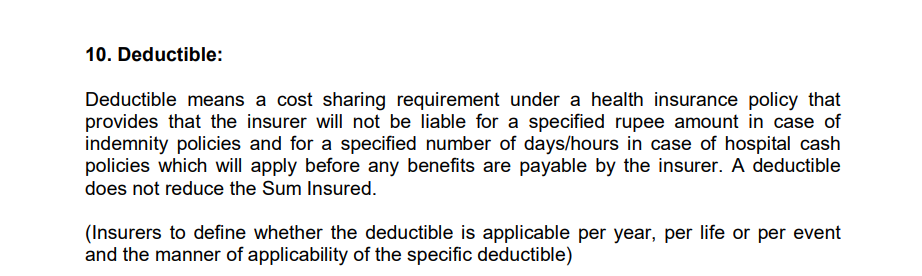
A deductible is the amount you pay first for a medical expense. The insurance company pays only after this amount has crossed. Deductibles appear in products like top-ups, super top-ups, base health plans, and hospital cash/benefit-based policies.
For example, if your health plan has a ₹2 lakh deductible and you incur a hospital bill of ₹5 lakh, you will pay the first ₹2 lakh, and the insurer will settle the remaining ₹3lakh.
Here’s a snippet how IRDAI, defines a deductible:
Types of Deductibles in Health Insurance Policies
How Does a Health Insurance Deductible Affect Your Premium and Claims?
The health premiums you pay may vary from plan to plan, but the general rule is simple. The higher the deductible, the lower the premium, because you’re agreeing to take on more initial cost.
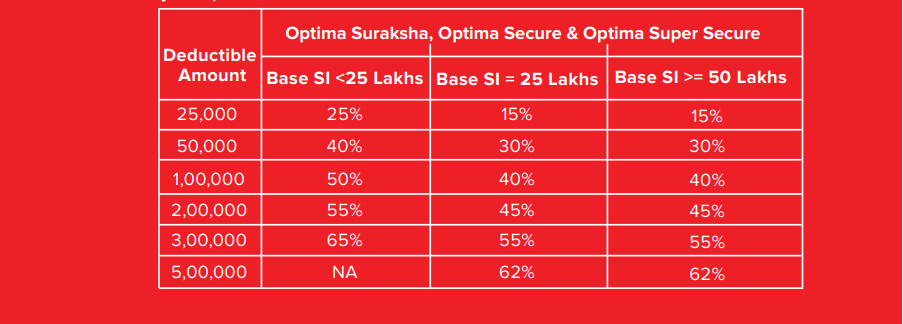
Here’s a snippet of the voluntary deductible offered by HDFC Optima Secure, where you get up to 65% discount on your premium:
Let’s see the scenarios that affect your health claim:
- Cashless Claims: The hospital collects the deductible amount from you before the insurer approves the balance. For example, on a ₹10 lakh bill with a ₹4 lakh deductible, you pay ₹4 lakh, and the insurer settles the remaining ₹6 lakh cashless.
- Reimbursement Claims: You pay the full bill initially. The insurer reimburses only the portion above the deductible. This applies to all deductible types, whether compulsory, voluntary, per-claim, or aggregate.
- With Employer Health Insurance: If you have employer health insurance along with a super top-up, the employer or base policy pays first. That claim amount helps meet the deductible, after which the super top-up covers the remaining expenses, if policy terms and policy years align.
Deductible vs Co-Pay vs Co-Insurance: What’s the Difference?
In case you opt for a deductible with your health plan, you pay an upfront amount before your health insurance starts covering costs. A co-pay is a fixed % of the bill you pay each time you use your health insurance. Co-insurance, largely a US concept, involves sharing costs by percentage after the deductible and is rarely seen in Indian health insurance plans.
Co-payment can feel heavier on large claims because it is a percentage of the bill, so your share increases as the hospital cost rises. An aggregate deductible is a fixed yearly amount, making your maximum exposure easier to predict and budget for(though total out-of-pocket can still vary due to other limits/non-payables).
How to Choose the Right Deductible in Health Insurance?
A deductible should not be picked just to lower your premium. It must match how likely you are to claim and whether you can comfortably pay that amount if a hospitalization occurs.
- If you don’t have a strong base cover, choose a comprehensive plan with minimal cost-sharing surprises.
- If you already have solid coverage through an employer or personal policy, a super top-up with a deductible equal to that base cover usually offers the best value.
- If premiums are very high (often for senior citizens), a deductible can help, but only if the deductible amount is affordable at claim time.
Reality Check: Ask yourself whether the premium savings over time are likely to be higher than the deductible you may need to pay. If you are not sure, avoid a high deductible.
Annual Premiums with Deductibles
Note: The listed premiums are of HDFC Ergo Optima Secure (15 lakh base cover, no add-ons, for a 30-year-old non-smoker male, residing in Delhi)
Insight: It’s a simple trade-off where you pay a lower premium today by choosing a deductible, but you take on a higher out-of-pocket cost when you make a claim, because the first ₹X is paid by you.
Why Talk to Ditto for Your Health Insurance?
At Ditto, we’ve assisted over 8,00,000 customers with choosing the right insurance policy. Why customers like Rajan below love us:

- No-Spam & No Salesmen
- Rated 4.9/5 on Google Reviews by 15,000+ happy customers
- Backed by Zerodha
- 100% Free Consultation
You can book a FREE consultation. Slots are running out, so make sure you book a call now or chat with us on WhatsApp!
Why Should You Opt for Deductibles in Health Insurance? Ditto’s Take
At Ditto, we usually avoid recommending deductible-based plans. For most people, choosing a deductible on a base health plan makes sense only if there exists a strong fallback cover (such as employer insurance) to absorb initial costs.
They also help if you have a solid emergency fund to handle out-of-pocket expenses, and you’re confident that hospitalizations will not be frequent.
If you are looking for a health plan from insurers with established track records, we recommend comprehensive plans for 2026, which align with your long-term goals. Explore more about how our experts evaluate health plans through Ditto’s cut.
Frequently Asked Questions
Last updated on:










